MedFriendly®


Basophil
A basophil is a type of white blood cell present in the
blood. White blood cells help protect the body against
diseases and fight infections. Basophils help protect the
body against disease and infections by eating some
types of bacteria, foreign substances, and other cells.
WHAT ARE SOME OTHER CHARACTERISTICS OF
BASOPHILS?
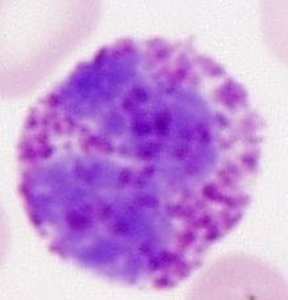
Basophils will look black and blue or dark purple when
stained by a basic dye, such as Wright stain. Dyes are
colored stains that are used in laboratories, often to tell
cells apart from one another. The nuclei of basophils
come in various forms. The word "nuclei" means more
than one nucleus. A nucleus is the center of a cell.
A basophil under the microscope.
FEATURED BOOK: Mosby's Diagnostic and Laboratory Test Reference
Thus, the centers of basophils appear in various forms. A unique characteristic of
basophils, compared to other white blood cells, is that they usually do not increase in
numbers in response to sudden infections or diseases. However, sometimes basophils
will increase in response to sudden infections or diseases. Another characteristic of
basophiles is that their cytoplasm (a gel-like substance that fills up a cell) is mostly made
of many large, rough-looking, grain-like particles. These grain-like particles can be seen
under the microscope, but may sometimes cover the nucleus. The grain-like particles may
decrease in numbers in response to allergic reactions and may increase in response to
some types of inflammation.
"Where Medical Information is Easy to Understand"™
The grain-like particles of basophils contain the following
substances: histamine, leukotrienes, and heparin. Histamine is a
substance found in all cells that is released during allergic and
inflammatory reactions. Leukotrienes are substances in the body
that produce allergic and inflammatory reactions, similar to
histamine. Heparin is a naturally occurring substance in the body
that prevents clotting (blood fluid coming together as a solid).
WHAT DOES A BASOPHIL LOOK LIKE?
A basophil is pictured above to the top right.
WHAT PERCENT OF WHITE BLOOD CELLS ARE BASOPHILS?
Approximately 0.4% to 1% of white blood cells are basophils. This is the normal range of basophils on
bloodwork tests. Basophils are the least common type of white blood cell.
WHAT CAN CAUSE THE LEVEL OF BASOPHILS TO BE TOO HIGH?
The level of basophils can be too high in response to an infection from a virus. Removal of the spleen can
also cause basophils to be too high. The spleen is an organ that helps fight infection and removes and
destroys worn-out red blood cells. Increased estrogen can cause basophils to be too high as well.
Estrogen is a type of hormone that promotes the growth of some physical female sexual characteristics.
Hormones are types of chemicals in the body that affect other cells.
Basophils can be high when inflammation in the body is healing. Basophils can also be high in diseases
that cause an increase in myeloid tissue. Myeloid tissue is a type of bone marrow (a tissue found inside
bones) that has many fibers. One such condition in which there is an increase in myeloid tissue is
polycythemia vera. Polycythemia vera is a condition of unknown cause in which there is a long-term
increase in red blood cells and other types of cells. Another such condition is myelofibrosis, in which the
normal bone marrow is replaced by fibrous tissue (the connective tissue of the body). Chronic myelocytic
leukemia (cancer of blood-forming tissues) can also cause a rise in basophils. Cancer is a group of
diseases in which symptoms are due to an abnormal and excessive growth of cells in one of the body
organs or tissues.
Basophils can also be increased due to some conditions that cause inflammation. Examples are asthma
(difficulty breathing due to narrowing of the airway passage), chronic dermatitis (a long-term inflammation
of the skin), and chronic inflammation of the sinuses. Sinuses are openings in the bone that often contain
fluid. Another inflammatory condition that can cause an increase in basophils is Crohn's disease. Crohn's
disease is a condition that causes inflammation of the intestine. The intestine is a tube shaped structure
that is part of the digestive tract. It stretches from an opening in the stomach to the anus (rear end) and
occupies most of the lower parts of the belly.
Hypothyroidism can cause basophils to be too high. Hypothyroidism is a condition in which the thyroid
gland is underactive. The thyroid gland is a butterfly-shaped organ located in front of the neck that
produces a natural chemical known as hormones that affect virtually every cell in the body and many
functions such as disease fighting, heart rate, energy level, and skin condition.
Hemolytic anemia can cause an increase in basophils. Hemolytic anemia is a disorder that causes the red
blood cells to be destroyed to early. Red blood cells help carry oxygen in the blood. Another cause of
increased basophils is Hodgkins lymphoma, which is a painless (yet very serious), worsening condition in
which lymphoid tissue is enlarged. Lymphoid tissue is a type of tissue that contains lympocytes.
Lympocytes are types of white blood cells that help the body fight against disease.
WHAT CAN CAUSE THE LEVEL OF BASOPHILS TO BE TOO LOW?
Basophils can be too low in people who have severe allergies. It can also be low in pregnant women and
people under stress. Hyperthyroidism can also cause basophils to be too low. Hyperthyroidism is a
condition in which the thyroid gland is overactive. See the previous section for a description of the thyroid
gland. Basophils can be low in people who are taking corticosteroids. Corticosteroids are a group of drugs
that act similarly to a natural chemical in the body known as corticosteroid hormone. Corticosteroid
hormones control the body's use of nutrients and the amount of water and salts in the urine.
WHAT ARE OTHER MEANINGS OF THE TERM, BASOPHIL?
Basophil is also used to describe any type of cell with grain-like particles in the cytoplasm (the gooey
substance inside of cells) that stain in a specific way when exposed to basic dyes. Dyes are colored
stains that are used in laboratories, often to tell cells apart from one another. Basophil is also used as an
adjective to describe parts of tissues that stain well when exposed to dyes. This meaning of basophil is
also known as basophilic.
WHAT ELSE ARE BASOPHILS CALLED?
Basophils are also known as a basophiles, basophilic leukocytes, basocytes, basophilocytes, and mast
leukocytes.
WHAT IS THE ORIGIN OF THE TERM "BASOPHIL"?
Basophil comes from the Greek word "basis" meaning "foundation," and the Greek word "philein" meaning
"to love." Put the two words together and you have "to love foundation."