MedFriendly®


Dacryoadenitis
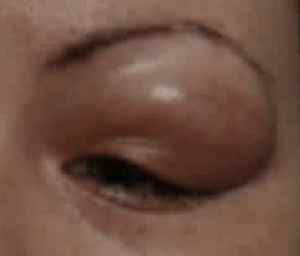
Dacryoadenitis is inflammation of a lacrimal gland(s).
Lacrimal glands are small organs in the eyes that
release tears.
WHAT CAUSES DACRYOADENITIS?
Acute (sudden onset) dacryoadenitis is caused by an
infection of bacteria (e.g., staphylococcus,
gonococcus) or a virus such as the flu or Epstein virus
(one of the most common viruses in humans). Other
examples of a viral infectious cause are the mumps and
parainfluenza.
FEATURED BOOK: Ophthalmology Made Ridiculously Simple
Mumps is a type of virus that occurs suddenly, mainly in children, and usually causes the
appearance of swelling in the face. Parainfluenza is a group of viruses that lead to upper
and lower respiratory infections. The infectious agent moves upwards from the
conjunctiva through small lacrimal ducts (tube-shaped structures) and into the lacrimal
gland. The conjunctiva is a layer that covers and protects the inside of the eyelids and
the front part of the sclera (the white part of the eyes).
When dacryoadenitis is a chronic (long-term) condition, it is usually not caused by an
infection but by an inflammatory condition. An example is sarcoidosis. Sarcoidosis is a
condition in which small, rounded bumps form on tissues.
"Where Medical Information is Easy to Understand"™
Another example is eye disease caused by an overactive thyroid
gland. The thyroid gland is a butterfly-shaped organ located in front
of the neck that produces a natural chemical known as hormones
that affect virtually every cell in the body and many functions.
Another example of a cause of chronic dacryoadenitis is orbital
pseudotumor, which is a swelling of tissue behind the eye in an area
known as the orbit (the bony opening in the skull where the eye is
located). Autoimmune disorders can cause dacryoadenitis. An
autoimmune disorder is one in which a person's organs or tissues
are mistakenly attacked by his/her immune system (defense
system). An example is Sjogren syndrome, in which the eyes and
mouth become excessively dry.
WHAT ARE SIGNS AND SYMPTOMS OF DACRYOADENITIS?
(sometimes with tenderness, pain, redness), excess tearing, or discharge. If the swelling is severe
enough it can cause distorted vision. Sometimes, there can be swelling of the lymph node in front of the
ear. Lymph nodes are small egg shaped structures in the body that help fight against infection.
HOW IS DACRYOADENITIS DIAGNOSED?
Dacryoadenitis can be diagnosed with a physical examination of the eye by a doctor or related health
care provider. The cause of the condition may be explored with a CT scan. CT (computerized tomography)
scanning is an advanced imaging technique that uses x-rays and computer technology to produce more
clear and detailed pictures than a traditional x-ray. Sometimes, a biopsy may be used to make sure that a
tumor of the lacrimal gland is not present and causing the inflammation, although this is a rare cause. A
biopsy is the process of removing living tissue or cells from organs or other body parts of patients for
examination under a microscope or in a culture to help make a diagnosis, follow the course of a disease,
or estimate a prognosis. Tumors are abnormal masses of tissue that form when cells in a certain area of
the body reproduce at an increased rate.
HOW COMMON IS DACRYOADENITIS?
Dacryoadenitis is not a common condition, particularly in African-Americans and children. One study
showed that only one in 10,000 ophthalmology patients had the condition. When the condition does occur,
it is usually on the left side in women over between 41 to 70.
HOW IS DACRYOADENITIS TREATED?
For viral causes of dacryoadenitis, applying warm compresses to the eyelids along with rest may be all
that is needed. Pain medications may sometimes be used. Otherwise, treating the underlying cause will
treat the condition. Antibiotics (e.g., Anoxicillin, Kephlex) may be used in cases of suspected bacterial
infection.
WHAT IS THE PROGNOSIS FOR DACRYOADENITIS?
Most patients will be completely cured of dacryoadenitis. In acute cases, it often resolves without
treatment. However, for the most serious causes of dacryoadenitis the prognosis depends on the
success of treatment of the underlying condition.
CAN DACRYOADENITIS BE PREVENTED?
Most cases of dacryoadenitis cannot be prevented. Some causes can be prevented, such as the vaccine
to prevent mumps or taking steps to prevent certain types of bacterial spread.
WHAT ELSE IS DACRYOADENITIS KNOWN AS?
Dacryoadenitis is also known as dacryadenitis.
WHAT IS THE ORIGIN OF THE TERM, DACRYOADENITIS?
Dacry- comes from the Greek word "dakryon" meaning "tear," the Greek word “aden” meaning “gland,” and
the word “it is” meaning “inflammation.” Put the words together and you get tear gland inflammation.