MedFriendly®


Macrencephaly
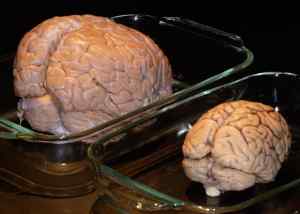
Macrencephaly is a condition present at or soon after
birth in which the brain is abnormally large. This can be
due to certain diseases that make the brain larger, such
as Alexander disease, later phases of Tay-Sachs
disease, and spongy degeneration of infancy.
Alexander disease is a slowly progressive and deadly
disease caused by the loss of the structure and
function of nerve cells. Tay-Sachs disease is a genetic
disorder that causes progressive deterioration of
mental and physical abilities.
FEATURED BOOK: Principles of Neurology by Adams and Victor
Spongy degeneration of infancy is a rare and deadly brain disease in infancy
characterized by nerve cell death and loss of myelin (a fatty covering of some nerve
cells) that gives the brain a spongy appearance (due to round spaces) and can also
cause paralysis (loss of movement and/or sensation) and blindness.
The large growth of the brain is macrencephaly is usually not due to the formation of
tumors, which are abnormal tissues that grow faster than other tissues. Macrencephaly is
associated with an abnormal enlargement of the head, which is known as macrocephaly.
Macrencephaly is also known as macrencephalia and macroencephaly. Macrencephaly
comes from the Greek word "makros" meaning "large," and the Greek word "enkephalos"
meaning "brain." Put the to words together and you get "large brain."
"Where Medical Information is Easy to Understand"™