MedFriendly®


Pneumonitis
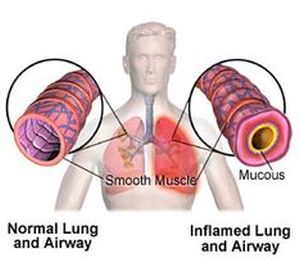
Pneumonitis is inflammation of the lungs. The lungs are
two organs in the body that help people breathe.
WHAT ARE SIGNS AND SYMPTOMS OF
PNEUMONITIS?
breathing, coughing (usually a dry cough), and
wheezing.
WHAT CAUSES PNEUMONITIS?
FEATURED BOOK: Muller's Diseases of the Lung
Pneumonitis can have many possible causes, such as infections, inhaling vomit, certain
allergic reactions to chemicals, and allergic reactions to plant or animal material that
contains dust. Allergic reactions to molds or bird droppings can also cause pneumonitis.
When allergies cause pneumonitis, this is commonly referred to as hypersensitivity
pneumonitis. When chemicals cause pneumonitis, this is sometimes referred to as
chemical pneumonitis.
Radiation exposure can also cause pneumonitis. Radiation is a type of energy in the form
of waves or streams of particles. When radiation causes pneumonitis, this is commonly
known as radiation pneumonitis. In August 2003, the Center for Disease Control reported
that 19 U.S. military personnel from Central Command developed sudden cases of severe
pneumonitis in both lungs.
"Where Medical Information is Easy to Understand"™
The patients required intubation (in which a tube needed to be
inserted down the windpipe) and mechanically assisted breathing.
Two of the 19 patients died. The cause has not yet been determined
to date, although some of the patients were found to be infected
with the following bacteria: Streptococcus pneumoniae, Coxiella
burnettii, and Acinetobacter baumannii.Thirteen of the 19 patients
were in Iraq when they developed pneumonitis. Fifteen of the 19
patients smoked cigarettes or cigars. All of the patients had been
exposed to heat, dust, and various pollutants in the environment,
such as smoke. Increased levels of eosinophils were noted in many
of the patients. Eosinophils are types of white blood cells present in
the blood.
White blood cells help protect the body against diseases and fight infections.
Pneumonitis can be caused as a rare side effect of some drugs, such as azathioprine and acebutolol.
Azathioprine is a medication that suppresses the body's immune (defense) system, usually to prevent
against rejection of transplants that the immune system may interpret as foreign. Acebutolol is a
medication used to treat high blood pressure.
WHAT ARE MORE SPECIFICS ABOUT THE INFLAMMATION IN PNEUMONITIS?
The spaces within the lung tissue are commonly affected in pneumonitis. The inflammation of the lung
usually causes the formation of scar tissue, and granulomas, especially of the bronchioles and alveoli.
Granulomas are accumulating groups of cells that are associated with chronic (long-term) inflammation
anywhere in the body. Bronchioles are small airways that branch off the bronchi. The bronchi are small
airways connected to the lungs. The alveoli are tiny sacs where gases are exchanged in the lungs so that
breathing can take place.
HOW IS PNEUMONITIS TREATED?
Treatment for pneumonitis depends on the causes. The goal is to remove from the person's environment
whatever has been determined to be causing the condition. Corticosteroids are usually administered to
decrease inflammation. Corticosteroids are a group of drugs that act similarly to a natural chemical in the
body known as corticosteroid hormone.
WHAT ELSE IS PNEUMONITIS KNOWN AS?
Pneumonitis is also known as pulmonitis.
WHAT IS THE ORIGIN OF THE TERM, PNEUMONITIS?
Pneumonitis comes from the Greek word "pneumon" meaning "lung," and the Greek word "itis" meaning
"inflammation." Put the words together and you have "lung inflammation."