MedFriendly®


Herpes Encephalitis
Herpes encephalitis is a suddenly occurring inflammatory
disease of the brain caused by direct invasion of the herpes
simplex virus. The herpes simplex virus is commonly known
for causing flu-like symptoms and cold sores. People usually
acquire the herpes simplex virus during childhood, but the
virus does not cause symptoms for many years until some
type of physical or emotional stressor activates it.
WHAT ARE THE SIGNS AND SYMPTOMS OF HERPES
ENCEPHALITIS?
Signs and symptoms of herpes encephalitis can include
fever, confusion, vomiting, tiredness, stiff neck, stiff back,
and delirium. Delirium is a state of fluctuating mental
confusion that develops over a few hours or days.
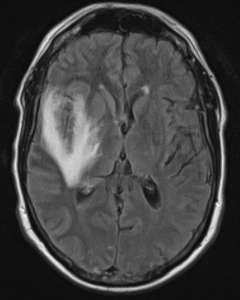
Brain MRI evidence (patchy white
areas) of herpes encaphalitis.
FEATURED BOOK: Herpes: Everything You Need to Know
WHAT KIND OF BRAIN DAMAGE DOES HERPES ENCEPHALITIS CAUSE?
Herpes encephalitis causes swelling of the brain and small bleeds in the cerebral cortex
(the top, main section of the brain), cerebellum, brain stem, and spinal cord. The
cerebellum is an area in the back, bottom part of the brain that is plays an important role
in movement and coordination. The brainstem is an area in the lower part of the brain that
connects it with the spinal cord. Loss of brain tissue will also occur when the brain is
attacked by the herpes virus.
"Where Medical Information is Easy to Understand"™
HOW IS HERPES ENCEPHALITIS DIAGNOSED?
Herpes encephalitis can be diagnosed after various steps are
undertaken. First, one needs to identify the signs and symptoms
mentioned above. As was stated earlier, the presence of seizures
early in the onset of symptoms is associated with herpes
encephalitis. Analysis of cerebrospinal fluid taken from the spine
can be analyzed for indications that the herpes virus is present.
Cerebrospinal fluid is the cushiony fluid that protects the brain and
spine from trauma. The spinal fluid is taken by a procedure known
as a lumbar puncture (spinal tap).
A lumbar puncture is a procedure in which a needle is inserted into a space inside the spinal canal for the
purpose of removing some of the cerebrospinal fluid. The spinal canal is the space between the spinal
cord and the bony structure that surrounds it.
Magnetic resonance imaging of the brain can be performed to rule out other possible causes of
symptoms, such as brain cancer. MRI scans produce extremely detailed pictures of the inside of the body
by using very powerful magnets and computer technology. As was mentioned in the last section, certain
areas of the brain become inflamed in herpes encephalitis. MRI scans can detect if swelling is present in
these areas.
HOW IS HERPES ENCEPHALITIS TREATED?
Herpes encephalitis needs to be treated as early as possible to prevent coma and permanent damage to
the brain and spine. A coma is a state of deep unconsciousness in which there are no voluntary
movements, no responses to pain, and no verbal speech. This is why early diagnosis is so important.
When herpes encephalitis is suspected, treatment involves administering antivirus medication. The
antivirus medication usually prescribed is acyclovir (Zovirax) and it is administered directly into the veins.
WHAT IS THE PROGNOSIS FOR PEOPLE WITH HERPES ENCEPHALITIS?
Prognosis is much better the earlier treatment begins. In fact, about 40% of patients will recover without
significant neurological side effects. Even with treatment, however, about 30% of patients will die from the
disease. Children and young adults have a better prognosis than older adults. However, infants are most
likely to develop permanent brain damage.
WHAT ELSE IS HERPES ENCEPHALITIS KNOWN AS?
Herpes encephalitis is also known as herpetic simplex encephalitis and acute inclusion body encephalitis.
WHAT IS THE ORIGIN OF THE TERM, HERPES ENCEPHALITIS?
Herpes encephalitis comes from the Greek word "herpes" meaning "a spreading skin eruption," the Greek
word “enkephalos” meaning “brain,” and the Greek word “itis” meaning “inflammation.” Put the words
together and you get “a spreading skin eruption (and) brain inflammation.”