MedFriendly®


Alanine aminotransferase
Alanine aminotransferase (commonly abbreviated
ALT) is a type of enzyme. An enzyme is a type of
protein that helps produce chemical reactions in the
body.
WHERE IS ALANINE AMINOTRANSFERASE
FOUND?
ALT is found in the blood serum. Blood serum is the
clear, thin, and sticky fluid part of the blood that
remains after the blood has changed from a liquid
into a solid form. ALT is also found in certain body
tissues, especially the tissues of the liver.
FEATURED BOOK: Mosby's Diagnostic and Laboratory Test Reference
The liver is the largest organ in the body and is responsible for filtering (removing)
harmful chemical substances, producing important chemicals for the body, and other
important functions.
ALT is found in smaller amounts in the heart, muscles, pancreas (a long organ in the
back of the belly), and the kidneys. The kidneys are two organs located on each side of
the spine, behind the stomach. The kidneys filter (remove) wastes from the blood.
"Where Medical Information is Easy to Understand"™
WHAT DOES ALANINE AMINOTRANSFERASE SPECIFICALLY
DO?
ALT helps to form a salt known as pyruvate and an amino acid
known as l-glutamate. Amino acids are groups of chemical
substances that form proteins. Proteins are extremely complex,
naturally occurring substances made of amino acids that are
essential to the body's structure and function.
ALT levels are measured alongside of asparate aminotransferase
(AST; another type of enzyme) levels to assess liver functioning.
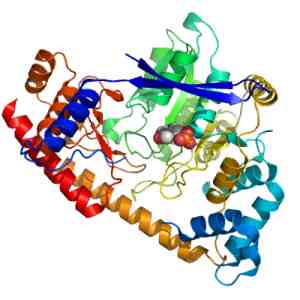
Structure of ALT
HOW DOES ALANINE AMINOTRANSFERASE DO ITS JOB?
ALT helps create the substances mentioned in the previous section by causing a chemical reaction. The
chemical reaction is caused by moving molecules from l-alanine (a type of amino acid) to alpha-
ketoglutarate (a type of salt). This reaction is reversible, however. Molecules are the smallest naturally
occurring particles of a substance. See the previous section for a definition of amino acid. The
molecules that ALT move are called amino groups. Amino groups are part of amino acids. They are
made up of one part nitrogen and two parts hydrogen. Nitrogen and hydrogen are both natural
elements. To sum it up, picture ALT as a builder that removes pieces from one structure to help create
another structure.
WHAT IS THE NORMAL LEVEL OF ALANINE AMINOTRANSFERASE IN THE BLOOD?
The normal range of ALT on blood work tests is less than 35 units per liter (U/L) or 5 to 35 International
Units per liter (IU/L). However, it is important to keep in mind that these ranges will be different
depending on the machine used to do the blood test. Always use the normal range printed on the lab
report to decide what range is normal. Regarding the way in which these ranges are measured, a unit is
a specific amount of a substance that is needed to produce a desired effect. A unit's value will differ for
each type of substance. An International Unit is very similar to a unit but is based on a different type of
scale. The value of an International Unit will also differ for each type of substance. A liter is a
measurement of the amount of space that a liquid takes up in a container, which is equal to 1.056688
quarts. To understand this better, picture a gallon of milk. It takes 4 quarts of milk to make up one gallon
of milk. Since one liter is a little bit more than one quart, 4 liters of milk is a little bit more than one gallon
of milk.
WHAT CAN CAUSE THE LEVEL OF ALANINE AMINOTRANSFERASE TO BE TOO HIGH?
To begin with, since there are many reasons why ALT levels can be high it is important that additional
testing is done to determine the exact cause. When an organ or body tissue is injured, increased levels
of ALT are released into the blood. The greater the degree of tissue damage, the greater the degree of
ALT that is released. When ALT is high, the most common cause is liver damage. The liver is the largest
organ in the body and is responsible for filtering (removing) harmful chemical substances, producing
important chemicals for the body, and other important functions. Long-term or sudden liver damage can
cause a rise in ALT levels.
Damage to other areas such as the heart, muscles, lungs, pancreas (a long organ in the back of the
belly) or the kidney, can cause the levels of ALT to increase. The kidneys are two organs located on
each side of the spine, behind the stomach. The kidneys filter (remove) wastes from the blood.
Inflammation of the heart can also cause high ALT levels. The ALT levels usually are only mildly
increased after a heart attack.
If the ALT levels are very high (up to 50 times higher than the normal range), chances are that the cause
is liver damage caused by viral hepatitis (an infection of the liver that causes liver inflammation), drugs,
or chemicals. People with hepatitis may have ALT levels that are 20 to 50 times higher than the normal
level. However, patients with tumors (types of abnormal tissue) of the liver or cirrhosis (a type of disease
that destroys the liver) usually only have ALT levels that are 2 to 4 times the normal level. People that
have mononucleosis may have high ALT levels. Mononucleosis is an abnormal increase in a type of
white blood cell in the blood. A cell is the smallest, most basic unit of life, that is capable of existing by
itself. White blood cells help the body fight against infections.
People who abuse alcohol may have mild to moderately increased ALT levels. In addition, high levels of
ALT can also happen when people drink too much alcohol and take acetaminophen. Acetaminophen is a
substance that fights against fevers and infections. An example of a medication that contains
acetaminophen is Tylenol. Taking narcotics can also cause ALT levels to be high. Narcotics are types of
substances or drugs that relieve pain and cause feelings of pleasure. Medications that can cause liver
damage may also lead to raised ALT levels. Such medications include heparin (a blood thinning
medication), tetracycline (a type of medication that fights infections), and metyhldpopa (a medication
used to treat high blood pressure).
Severe burns, shock, and polymyositis can cause high ALT levels. Polymyositis is an inflammation of
many muscles, and is usually accompanied by deformity, abnormal fluid buildup in tissues, difficulty
sleeping, tension, sweating, and pain. Dermatomyositis, which a disease that causes destruction of
muscle tissue, can also raise ALT levels. Rapid growth can cause mildly increased ALT levels, especially
in pregnant women and young children. High ALT levels can be caused by seizures (sudden, violent,
involuntary muscle movements). A type of infectious virus known as Epstein-Barr virus can also cause
high levels of ALT.
WHAT CAN CAUSE THE LEVEL OF ALANINE AMINOTRANSFERASE TO BE TOO LOW?
Low levels of ALT are normally found in the blood. Thus, it is not usually a cause for concern. However,
a low ALT level can be caused by poor nutrition. A low ALT level can also be caused by infections of the
urinary tract. The urinary tract is the part of the body that deals with the formation and excretion of urine
(pee). To excrete means to release from the body as waste.
WHAT CAN CAUSE ALANINE AMINOTRANSFERASE LEVELS TO BE INACCURATE?
Sometimes, there are factors that do not involve the patient that can cause the test results to be
inaccurate. These factors include rough handling, improper refrigeration, or contamination of the blood
sample.
WHAT ELSE IS ALANINE AMINOTRANSFERASE CALLED?
Alanine aminotransferase is also known as glutamic-pyruvic transferase (GPT), serum glutamic-pyruvic
transferase (SGPT), and alanine transaminase.